No products in the cart.
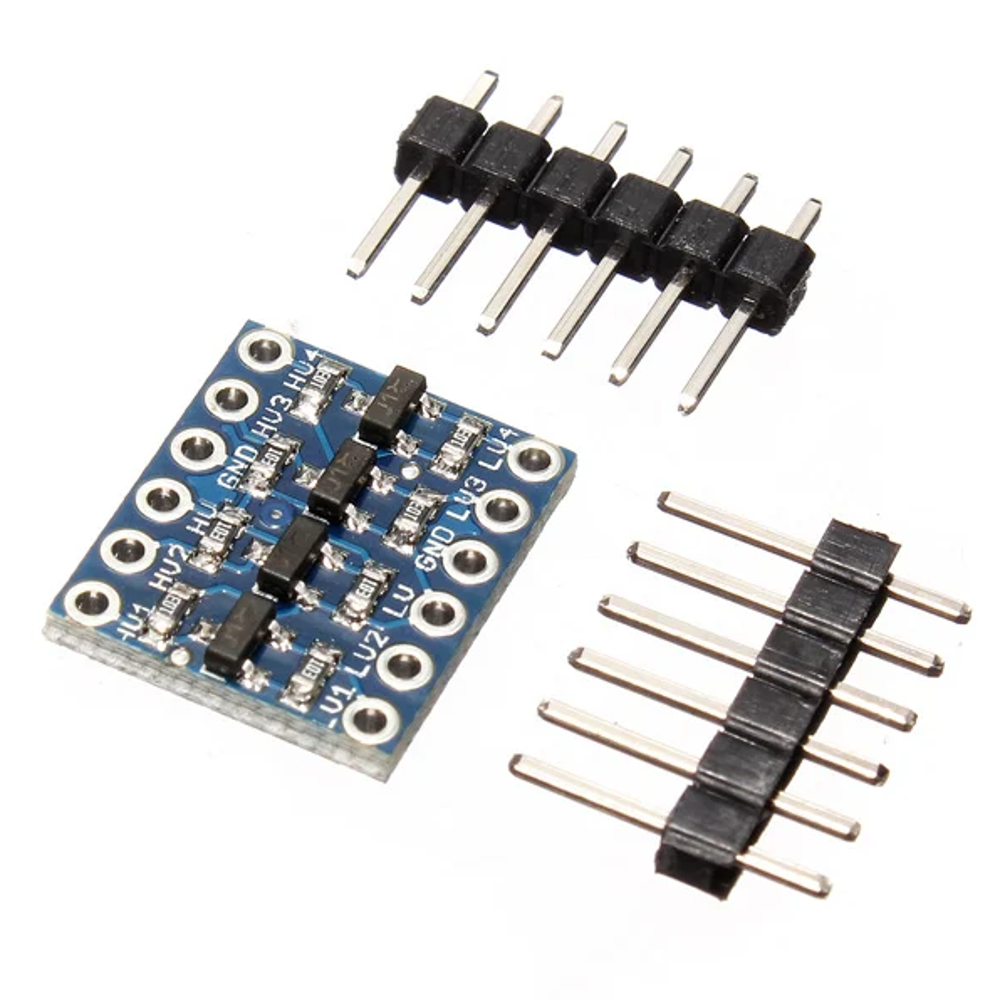
I2C Bi-Directional logic Level Converter-4 Channel
In Stock
In Stock
Add to Wishlist
CompareAdd to Wishlist
- Mutual transform between 5V TTL and 3.3V TTL
- Four channels of logic and high voltage low voltage logic can two-way transform
- Portable and lightness, with 2 rows 6 pin contact pin
- I2C Bi-Directional logic Level Converter-4 Channel
Description
- Purpose: It is used to interface I2C devices operating at different logic voltage levels. For example, you can connect a 3.3V I2C device to a 5V microcontroller or vice versa.
- Channel Count: This converter typically provides 4 channels, allowing you to convert logic levels for up to four I2C devices simultaneously.
- Bi-Directional: It supports bidirectional communication, meaning it can handle both data transmission and reception between devices.
- Voltage Compatibility: It usually supports at least two different voltage levels, such as 3.3V and 5V, but some models may offer more voltage options.
- Schematic: The converter typically employs a combination of level-shifting MOSFETs or other components to safely translate logic levels between devices.
- I2C Compatibility: It is designed to work specifically with I2C communication, which requires bidirectional data lines (SDA and SCL).
- Simple Connection: Typically, you connect the lower voltage side to your lower voltage I2C device and the higher voltage side to your higher voltage device or microcontroller.
- No External Power Required: Most I2C level converters draw power directly from the connected devices, so there’s no need for an external power supply.
- Pull-Up Resistors: Some models may include pull-up resistors on the I2C lines to ensure signal integrity.
- Low Signal Delay: These converters are designed to introduce minimal delay in the I2C communication, ensuring that data transmission remains efficient.
- Compact Form Factor: They are often available in compact, easy-to-use breakout board designs, making them suitable for breadboarding and prototyping.
- Voltage Tolerance: Check the specifications for the specific voltage tolerances, as they can vary between different models.
- Compatibility: Ensure that the converter you choose is compatible with the voltage levels of your I2C devices and adheres to your project’s requirements.
- Datasheet: Always refer to the datasheet or documentation provided with the specific converter model you are using for detailed connection instructions and specifications.
- Applications: These converters are commonly used in projects where different I2C devices with varying logic voltage levels need to communicate with each other, such as in sensor interfacing, microcontroller-based systems, and embedded projects.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.